7 SaaS B2B Key Performance Metrics to Unlock Growth Like a Unicorn
Your marketing strategy should align with your company goals. While ROI (return on investment) is important, you also want to reach new customers and convert them into paying clients. How do you measure success?
You might already be using some metrics to track your SaaS performance. But if you want to take things to the next level, you’ll need to focus on these seven vital metrics or KPIs (Key Performance Indicators).
1. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
The customer acquisition cost is the average cost of acquiring one user by making them a subscriber.
This includes all costs associated with getting someone to sign up for your service, such as advertising expenses, sales team time, etc. It’s important to know this number because it will help you determine how much money you’re spending per user.
The formula to calculate your Customer Acquisition Cost is to divide the sum of your Marketing and Sales expenses by the number of customers acquired during that period.
A high customer acquisition cost will eat up your profits and can push your SaaS business into a loss.
However, a consistently reducing CAC quarter over quarter while increasing your revenue is a good indicator. It means that you effectively scale up your SaaS business and increase your profitability.
Best Ways to Reduce Your Customer Acquisition Cost
A high Customer Acquisition Cost is usually a result of ineffective marketing and sales practices.
Creating brand awareness and high-quality lead generation eats up most of the marketing and sales budget and increases the Customer Acquisition Cost.
To reduce your CAC, you need to: Target and reach the right audience, simplify and optimize your sales process, make your value proposition clear, and create a cost-effective marketing strategy.
Targeted content marketing is one of the cost-effective ways to acquire SaaS users for your product.
You can employ Search Engine Marketing, Email Marketing, Video Marketing, and social media marketing strategies to increase your brand exposure and push more high-quality leads into your sales funnel.
2. Product Adoption Rate
Product adoption rate is the ratio of the number of new users to the total number of users of your product.
It is a direct growth indicator for your product and it is different from customer acquisition. If you have a low product adoption rate, you may not be reaching out to the right audience. You may need to improve your onboarding experience, add features, and provide better support.
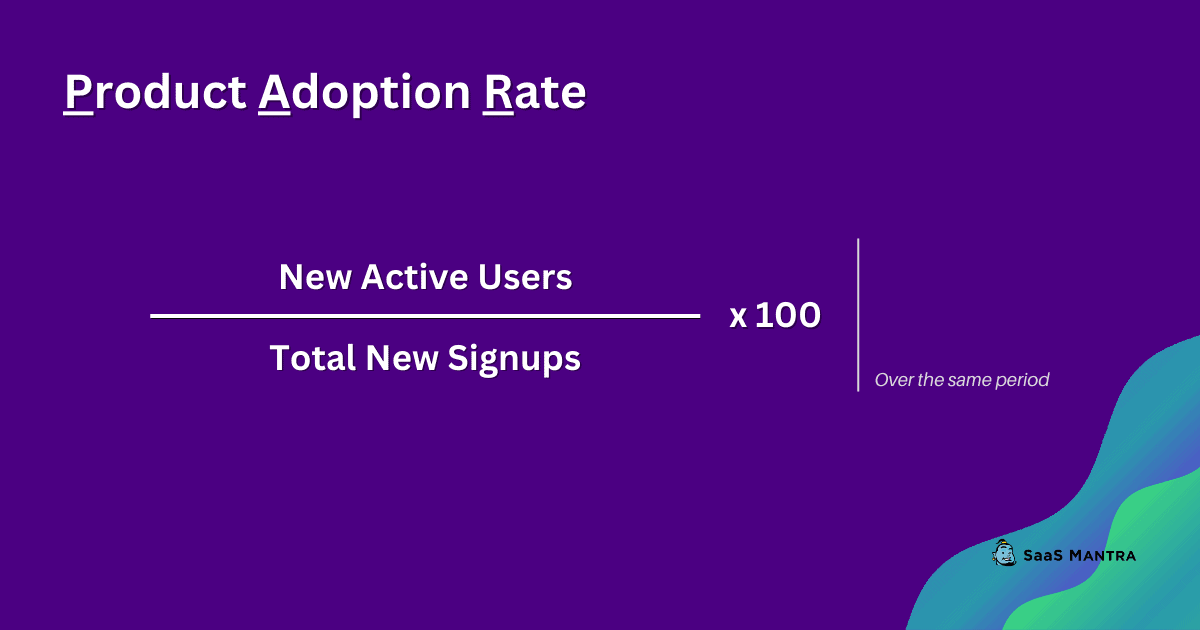
If you see a consistent increase in your product adoption rate, then you’re doing well. However, if you notice a decrease in your product adoption rate over time, you may need to rethink your marketing strategy.
To attain the flywheel effect in your business, you need to increase your product adoption rate and keep it higher than your churn rate.
3. Customer Retention Rate
It is the rate of customers you have retained over a period.
Did you know that acquiring a new customer costs 5x more than retaining an existing customer?
Also, it is easier to convert an existing customer than a new customer. Hence retaining your existing customers is an effective way to increase your revenue with a high ROI.
The customer retention rate is measured over different specific periods. It can be a 1-week retention rate, a 1-month retention rate, etc. Customer retention is the key to the long-term success of any SaaS company.
You can calculate your customer retention rate by dividing the number of users at the end of the calculating period by the number of users at the beginning of the period.
Improving your Customer Retention Rate helps decrease your Customer Churn Rate and increase your ARR. This, in combination, with a high product adoption rate helps scale your SaaS company and flywheel it.
4. Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
Annual recurring revenue or ARR is the amount of money you get every year from your current subscribers/customers.
The recurring revenue model of the SaaS industry gives users flexibility and reduces risk, while bringing financial stability to the SaaS companies.

ARR is calculated by aggregating your Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) over a period of 12 months. Hence you can increase your ARR by focusing on increasing your Monthly Recurring Revenue.
If you want to grow your business, you should focus on increasing this metric. You can use ARR to identify all the viable growth options and develop your strategy based on that.
It is also important to note that ARR does not include the initial purchase price of your product.
5. Customer Churn Rate
Customer churn rate is the percentage of users who leave your service in a specified period of time.
Since the SaaS business model relies on recurring revenues, decreasing your churn rate is critical to sustaining and increasing your revenue.
The churn rate gives you insights into the effectiveness of your customer retention measures. If you are losing too many customers, you might need to reevaluate your marketing and customer retention strategy.

When a company has a high and increasing churn rate, it is what you call the company’s bleeding customers. And you need to take immediate and drastic measures to keep your company afloat and competitive.
A high churn rate means that your customers are leaving your service because they no longer find your value proposition impressive or they find another solution that works better for them.
As you know that retaining an existing customer is much cheaper than acquiring new ones; paying attention to your churn rate really pays you. In other words, decreasing your churn rate helps you increase your Customer Lifetime Value.
6. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer lifetime value (CLV) is the total revenue you can expect from a customer during their relationship with your business—i.e. before they churn.
This metric is very useful when you want to understand how much potential profit you have lost due to churning.
In order to calculate CLV, we first need to calculate MRR. Then we add up the MRR of each user and divide it by the length of their subscription.
A general rule of thumb is to keep your Customer Lifetime Value higher than your Customer Acquisition Cost. However, as a SaaS business, you also need to factor in the operating cost of serving the customer during their lifetime as a customer.
In other words, your Customer Lifetime Value needs to be higher than the sum of Customer Acquisition Cost and the operating cost per customer for your business to be profitable.
7. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
The Net Promoter Score is a metric that quantifies your customer satisfaction and the likelihood that they will recommend your product to someone.
It measures the satisfaction of your customer with a simple survey question. The question can be as simple as “How likely are you to recommend ‘xxx’ product to a friend or a colleague?”.
The customers choose their response on a scale of 0-10. A score of 0 is less likely, while 10 is extremely likely.

Customers who respond with a score in the range of 8-10 tend to be more satisfied with your business and may even encourage others to use your product.
You can use the NPS to improve the brand loyalty of your customers.
For example, whenever someone is dissatisfied with your product and responds with a lower score, you can ask them a follow-up question. it can be something like “What can we do to improve your experience with us?”
You can improve your Net Promoter Score by working on those responses and eventually the brand loyalty of your customers.
Final Word
There are many ways to measure the performance and success of your SaaS business.
You should always look at all these metrics and try to optimize them so that you can achieve maximum growth.




