Should US-based (and Non-European) SaaS Companies Comply with GDPR?
Here’s what you should know about GDPR compliance for a US-based SaaS company.
This post will answer your question regarding the data protection law to make an informed decision before launching your SaaS for Global users.
Since the GDPR is a European Union law, any SaaS company outside the European Union can make use of this information. Hopefully, it will help you save millions in GDPR penalties and prevent worst-case scenarios.
What is GDPR Compliance?;
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is the data protection law of the European Union which mandates businesses and organizations in the region to follow a set of defined rules. It gives the end-users better data privacy, protection, and control over their data.
GDPR came as a successor to the preceding Data Protection Directive of 1995 when it was enforced on 25 May 2018.
The new regulation has been designed to give more power to individuals by giving them access to their personal information, the right to be forgotten, and the ability to have their data deleted.
Widely regarded as the golden standard of data protection laws, GDPR is transforming the global digital data protection infrastructure.
What does it mean for companies outside the EU?
Or you may be wondering, can GDPR be enforced in the US?

Should a US-based SaaS Company Comply with GDPR?
How does GDPR compliance in US work?
US-based SaaS companies are not obligated to comply with GDPR by default. However, as a SaaS business, it makes sense to comply with GDPR to your advantage.
It is because GDPR applies to all companies that are based in the European Union or offer services to the citizens of the EU.
So, who needs to be GDPR compliant?
It’s time to stop thinking that GDPR applies only to EU-based businesses. Instead, if you provide services to customers in the EU, you also must comply with GDPR.
The compliance includes providing GDPR-recommended data security infrastructure, customer support, routines to follow to ensure data protection, and SOP in case of a security breach.
In short, if you have any business operation in any of the European Union member states, you need to comply with GDPR. And given the hyper-connected digital business environment, your SaaS business has more to gain by complying with GDPR than not.
What if Your SaaS doesn’t Comply with GDPR?
If you are not GDPR compliant, you could face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global revenue, whichever is greater.
However, the GDPR article 30(5) gives an exception.
The clause gives an explicit exemption from GDPR compliance for businesses operating with fewer than 250 employees.
Though businesses with less than 250 employees do not have to comply with GDPR, it changes on one condition. If your SaaS handles sensitive data that deals with the rights and freedom of individuals, data relating to criminal convictions, handling other special categories of data, and regular processing of data, you must have systems in place to comply with GDPR.
If your SaaS Startup lies in this narrow window of exemption, your SaaS will be free of any legal obligations. Hence, you may overlook GDPR compliance entirely.
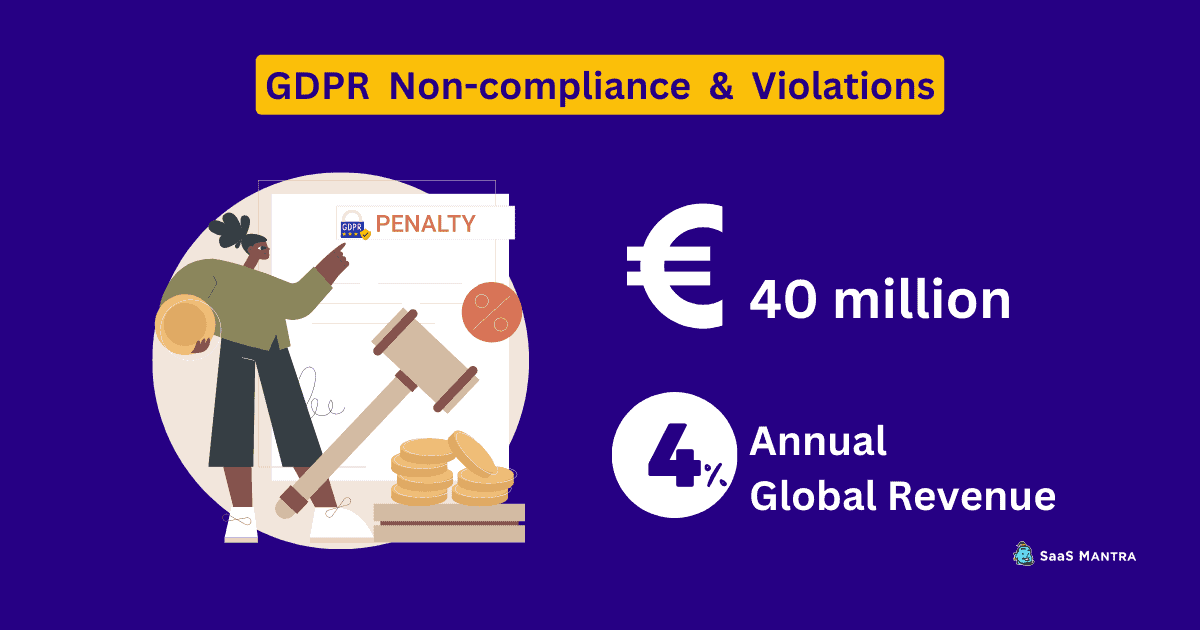
Before you choose to skip GDPR compliance for your US-based SaaS, you must consider this.
Customers, especially B2B customers, are more privacy-conscious than ever. Even if your target market is outside the EU, your customers are likely to expect you to be GDPR compliant. GDPR compliance costs money in the beginning; there’s no doubt. Complying with GDPR, even as a small startup business, helps you position your product in the market and make it more desirable for your audience compared to a competitor.
Moreover, as data protection and privacy laws evolve, it is likely that you will be required to comply with these standards.
How Can Your SaaS Comply with GDPR?
There are three main ways to comply with GDPR. Let’s take a look at each of these options.
1. Implementing Privacy By Design (PbD) in the Cloud
Privacy by design is a concept where every aspect of your product is built around protecting user data. It means that you should build your application with privacy in mind from the beginning. This way, you can avoid having to change your app later when you realize that you were wrong about how users would use your product.
For example, let’s say you’re building a community app. You might want to allow users to post photos and videos or even chat with each other directly. But then you find out that people don’t like posting their personal information online. So instead of sharing their personal details, you decide to limit the features of your app. It gives users the power to let people see what they allow to see.
This kind of approach is called “privacy by design”.

It’s important to note that PbD does not mean that you have to build everything from scratch. There are many tools available to help you implement PbD. For example, Google Analytics allows you to track all sorts of user behavior and collect data without collecting personally identifiable information.
You can also use third-party services such as Facebook Login, which lets you integrate your login process into Facebook.
It’s worth noting that PbD is not just limited to software development. Any company that collects data needs to follow PbD principles.
2. Using Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
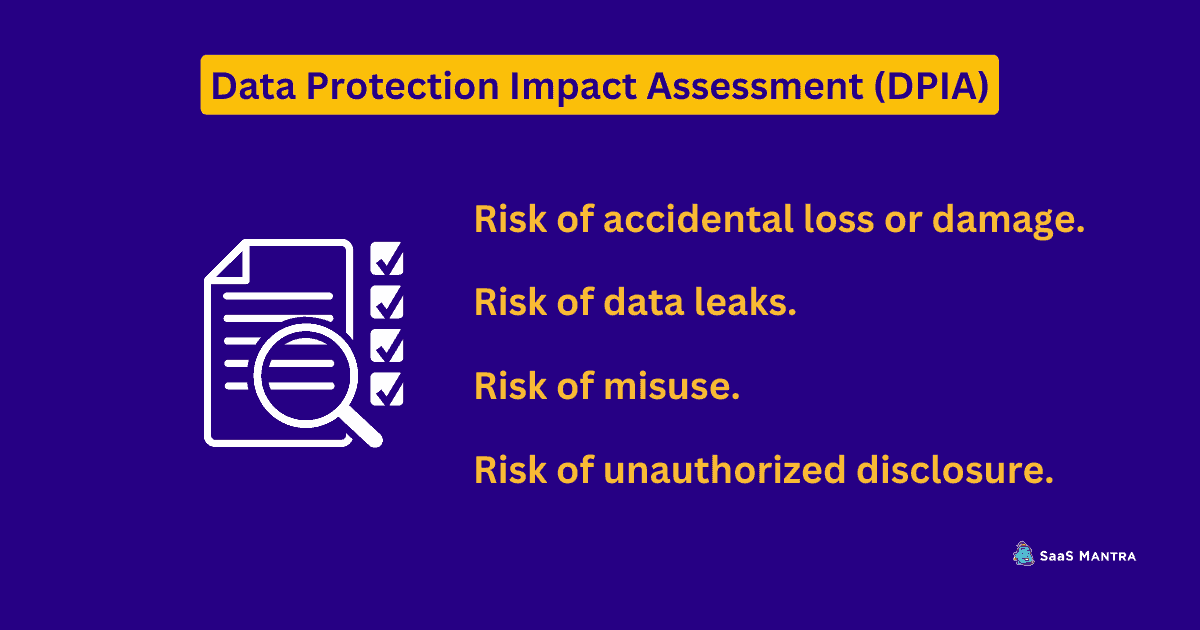
Data protection impact assessment (DPIA) is another tool that you can use to assess the risks associated with your data collection practices. DPIA is an independent assessment of the potential impacts of your data collection activities on individual rights.
The European Union has defined four types of risk:
• Risk of accidental loss or damage
• Risk that someone else could access your data
• Risk of misuse
• Risk of unauthorized disclosure
If you fail to address one of these risks, you’ll be violating GDPR.
In order to do a proper DPIA, you need to know precisely who your customer base is. The first step is to identify your target audience.
Next, you need to understand what data you collect from your users.
Then you need to determine whether this data is sensitive. If it is, you must consider the implications of sharing it.
Finally, you need to think about how you will protect this data.
Once you’ve completed your DPIA, you’ll be able to create a plan to mitigate any risks.
3. Having a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
A DPO is a person who is responsible for ensuring compliance with the GDPR. They ensure that companies are following the rules set forth by the EU.
A DPO can be anyone from a senior executive to a junior employee. A DPO may also be a third-party organization.
There are two main roles that a DPO plays under GDPR:
• Ensuring that the organization is compliant with the law
• Providing advice to businesses on best practice

How to Check GDPR Compliance?
For better flexibility and cost-effectiveness, it makes sense to have an in-house Data Protection Officer.
But you cannot appoint anyone as a Data Protection Officer for your SaaS Startup. A DPO has to be GDPR certified by passing the GDPR exam.
Moreover, GDPR requires the DPO to be free of any other responsibilities to avoid conflict of interest with their data protection and monitoring responsibilities.
These steps may sound exhausting for a SaaS Startup to comply with the GDPR and remain GDPR compliant. Practice the following steps to avoid any unintentional GDPR compliance violation and its consequences.
Final Word
General Data Protection Regulation is a futuristic step towards data protection that is changing the SaaS landscape for both US-based SaaS companies and the rest of the world. It’s important to stay up-to-date with the latest standards so that you don’t get caught off guard as it evolves and your customers adapt to it.
If you are a US-based or a non-EU SaaS developer, how are you implementing GDPR for your SaaS product?
Share your thoughts and the common challenges you’ve faced in complying with GDPR.